Kingsgrove Branch:
Safety Tape
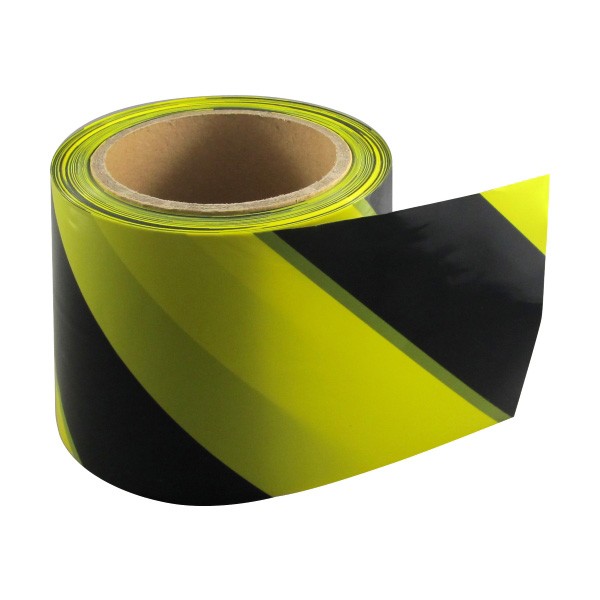
In the comprehensive framework of Australian Work Health and Safety (WHS) legislation, the mitigation of risk relies on a structured Hierarchy of Controls. While engineering controls eliminate hazards at the source, administrative controls are essential for managing residual risk. The deployment of industrial Safety Tape constitutes a critical administrative control, serving as the primary visual interface between the facility infrastructure and the workforce. Far from being a generic consumable, professional-grade safety tape is an engineered product governed by strict standards regarding chromaticity, luminosity, and slip resistance. For facility managers, safety officers, and electrical contractors, understanding the material science of PVC substrates, the classification of anti-slip grits under AS 4586, and the durability requirements for high-traffic environments is essential for maintaining a compliant and accident-free workplace.
The Chromatic Standard: AS 1319 Protocols
The efficacy of any visual warning system is predicated on immediate, subconscious recognition. Australian Standard AS 1319 (Safety signs for the occupational environment) dictates the colour coding protocols used to convey specific information. These standards extend to the application of adhesive tapes used for floor marking and hazard identification.
- Yellow and Black Diagonal: This is the universal designator for "Caution." It is mandated for marking physical hazards such as low headroom, changes in floor level, or the perimeter of mobile plant operation zones.
- Red and White Diagonal: This signifies "Danger" or fire protection. It is used to demarcate areas where entry is prohibited or to keep the area clear around fire extinguishers and hose reels.
- Green and White: Used to identify the location of safety equipment, such as First Aid kits, eye wash stations, or emergency egress routes.
Compliance requires that the tape maintains these colours without fading. Inferior tapes often suffer from UV degradation, turning safety yellow into a pale white. Professional-grade tapes typically utilise a "reverse print" or laminated construction, where the pigment is protected under a clear wear layer, ensuring the safety message remains visible even after heavy abrasion.
Floor Marking and Traffic Durability
In logistics centres and manufacturing plants, floor marking tape replaces painted lines due to its modularity and ease of application. However, the mechanical stress placed on these tapes by forklift tyres and pallet jacks is immense.
The failure mode of standard vinyl tape is typically "shear" or "lift." When a forklift wheel turns on the tape, the torsional force can rip the adhesive from the concrete. To combat this, heavy-duty industrial tapes employ a bevelled edge design and a recessed adhesive profile. Schnap Electric Products manufactures a range of high-traffic floor tapes constructed from rigid PVC with aggressive rubber-based adhesives. These tapes are engineered to resist the "scuffing" action of industrial machinery, ensuring that aisle markings and pallet bays remain clearly defined, which is a key requirement for traffic management plans.
Anti-Slip Technology and AS 4586
Slips, trips, and falls remain a leading cause of workplace injury in Australia. The application of anti-slip safety tape is a critical countermeasure, particularly on stair nosings, ramps, and ladder rungs. This application is governed by AS 4586 (Slip resistance classification of new pedestrian surface materials).
Technically, these tapes consist of a carrier film coated with a mineral aggregate, typically aluminium oxide or silicon carbide. The "grit size" determines the coarseness and the friction coefficient.
- Standard Grit (60 Grit): Suitable for general internal use on stairs and walkways.
- Coarse Grit (36 Grit): Required for external environments or areas prone to heavy contamination, such as oil or mud.
The bonding of the grit to the carrier is the quality differentiator. In cheaper tapes, the grit sheds rapidly under foot traffic. Schnap Electric Products anti-slip tapes utilise a high-bond resin system that locks the mineral aggregate to the substrate, ensuring long-term performance. Furthermore, for electrical substations and switchrooms, Schnap Electric Products offers specific non-conductive anti-slip tapes to ensure that the safety measure does not introduce an electrical hazard.
Photoluminescent Systems for Egress
In the event of a power failure, the safe evacuation of a facility relies on emergency lighting and photoluminescent (glow-in-the-dark) guidance systems. Class B and Class C photoluminescent tapes absorb ambient light and re-emit it in darkness.
These tapes are frequently applied to skirting boards, door frames, and handrails to outline the escape path. The luminance decay time is the critical specification. High-performance tapes can remain visible for several hours after the lights go out. Facility managers must ensure that the tapes selected meet the luminance requirements of the National Construction Code (NCC) for the specific building class.
Surface Preparation and Adhesion
The most common cause of safety tape failure is poor surface preparation. Concrete floors in industrial settings are often impregnated with oil, moisture, or curing agents.
Professional application protocols mandate the use of an isopropyl alcohol cleaner or a dedicated primer to raise the surface energy of the substrate before application. When sourcing these critical safety supplies, contractors typically visit a specialised electrical wholesaler to procure not just the tape, but the compatible primers and edge-sealing compounds. Ideally, an edge sealer should be applied to the perimeter of the tape to prevent water and cleaning fluids from migrating under the adhesive, which causes the tape to lift over time.
Conclusion
The deployment of safety tape is a calculated engineering decision that directly impacts the risk profile of a facility. It serves as a constant, passive instruction to the workforce, guiding behaviour and highlighting danger. Its effectiveness relies on strict adherence to AS 1319 colour codes, the selection of appropriate anti-slip grades, and the use of robust materials capable of withstanding industrial wear. By utilising high-quality, compliant marking solutions from trusted brands like Schnap Electric Products, industry professionals can ensure that their safety systems are visible, durable, and effective in protecting human life. In the visual language of safety, clarity is non-negotiable.
Recent posts

Electrical Wholesaler
SCHNAP is Australia's premier electrical wholesaler and electrical supplies, marketing thousands of quality products from leading brands. Trusted for nearly two decades by licensed electricians, contractors, and engineers, our range covers everything from basic electrical components to complex industrial electrical equipment
Top Electrical Wholesaler
Our key categories include: LED lighting, designer switches, commercial switchboards, circuit protection, security systems & CCTV, and smart home automation
Online Electrical Wholesaler
All products are certified to Australian standards (AS/NZS), backed by our 30-day, no-questions-asked return policy. Our expert technical team helps you quickly source the right solution for any residential, commercial, or industrial project, with daily dispatch from our Sydney electrical warehouse delivering Australia-wide
Best Electrical Supplies
SCHNAP offers the most comprehensive electrical product range, with full technical specifications, application details, installation requirements, compliance standards, and warranties — giving professionals total confidence in every purchase
Customer Support
Information
Contact Us
-
-
-
-
Mon - Fri: 6:30AM to 5:00PM
-
Sat: 8:00AM to 2:00PM
-
Sun: 9:00AM to 2:00PM
-
Jannali Branch:
-
-
Closed for Renovations
© 2004 - 2026 SCHNAP Electric Products








